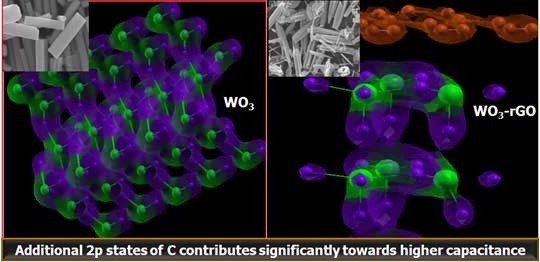
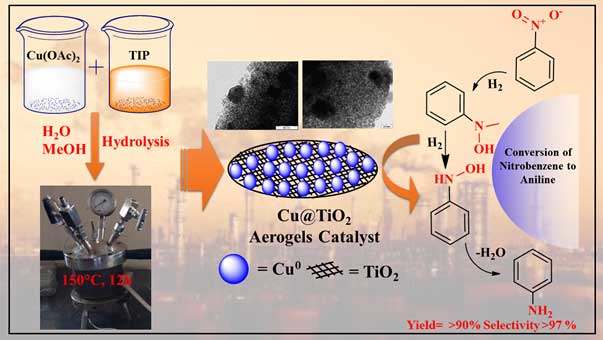
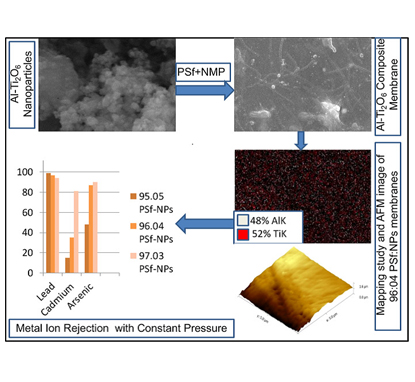
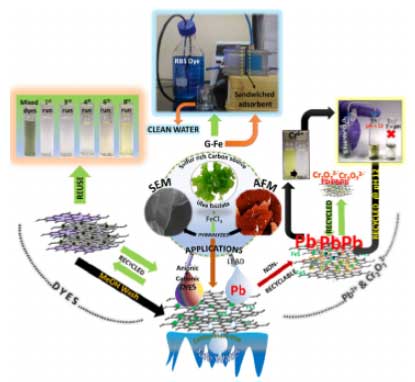
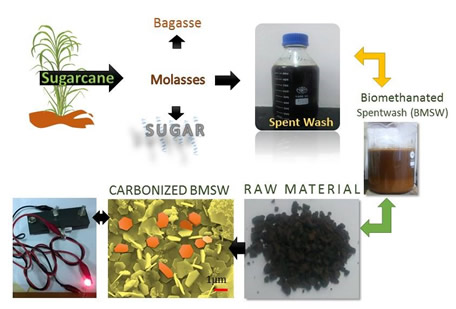
|
|
|
Research Highlights
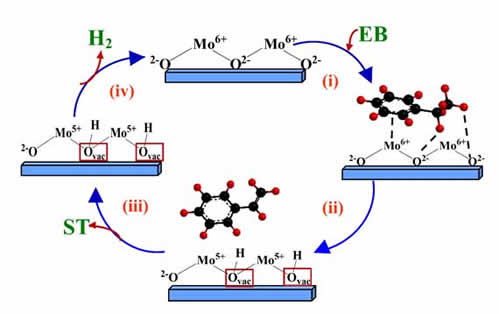
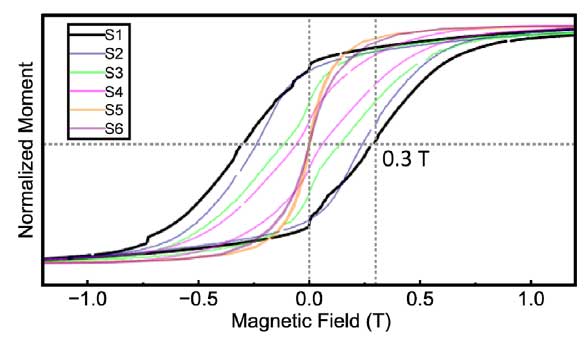
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak’s research group has recently published a research article in Small (2025), e09637, titled “Unlocking High Coercivity at Room Temperature in Phase-Modified MoS₂.” The study reports room-temperature ferromagnetism in phase-modified 1T-MoS₂, exhibiting one of the highest coercivities reported to date (~0.3 T). The results suggest that strain-driven magnetic anisotropy plays a key role in the observed enhancement of coercivity, highlighting phase engineering and strain modulation as effective routes for realizing robust room-temperature magnetism in two-dimensional materials.
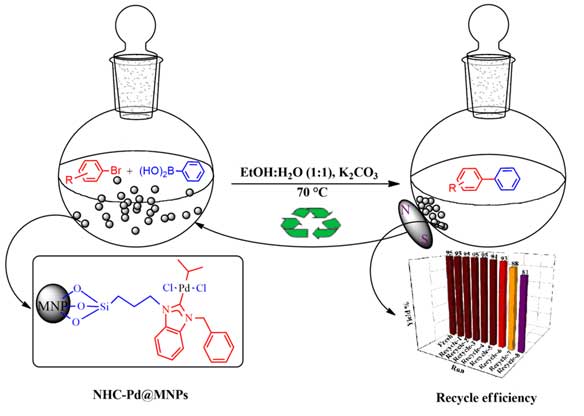
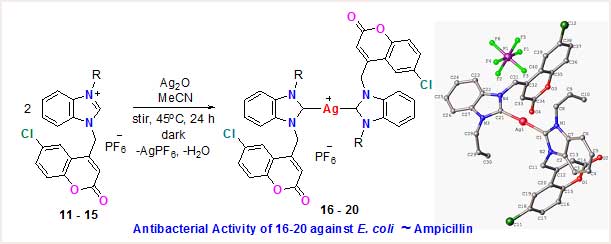
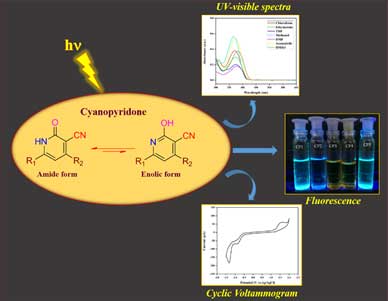
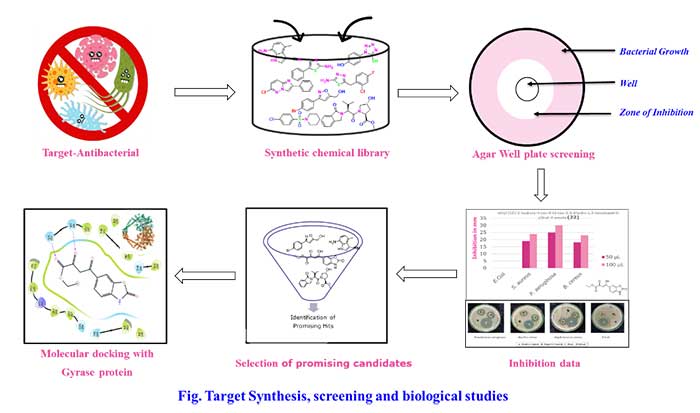
- Dr.Ramesh Dateer and Collaborators published the research article in Journal of ‘Molecular Structure’ entitled “Design, synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial activity with library of N, O and S-containing heterocyclic compounds” Herein, a series of fused heterocyclic compounds were synthesized and evaluated for antibacterial activity against gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus) and gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacterial strains. Among the library of synthesized molecules, the minimum inhibitory concentration and inhibition study demonstrated the most promising broad-spectrum activity.
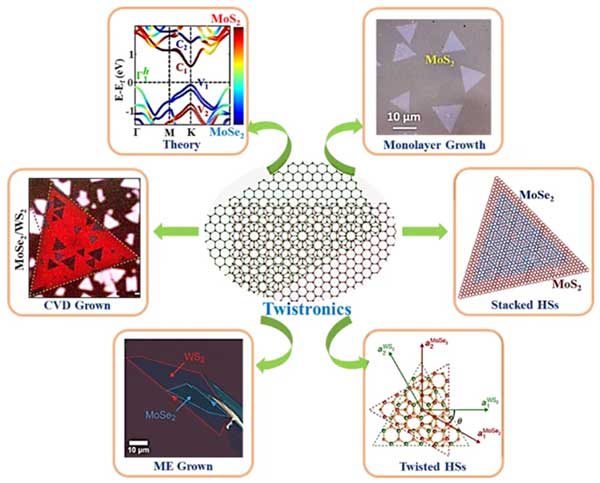
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak’s research group has recently published a review article in Discover Nano (2025) 20, 169, titled “Recent development in the synthesis of twisted Van der Waals heterostructures”. This article provides an overview of the latest progress in the synthesis and growth of twisted van der Waals heterostructures (t-vdW HSs), with particular emphasis on chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and mechanical exfoliation (ME). It also highlights other significant techniques such as metal–organic CVD (MOCVD) and molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). We hope this contribution will serve as a useful reference for the global 2D materials research community.
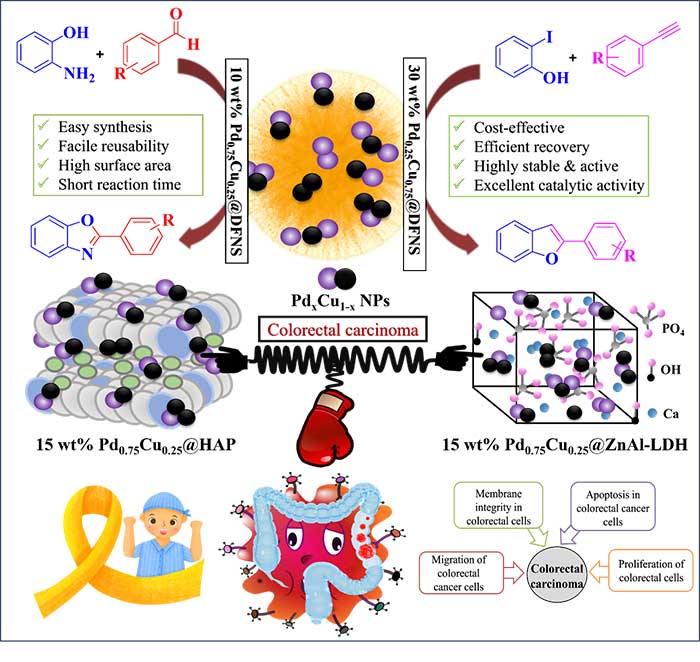
- Prof. Siddappa A. Patil’s research group has recently published a research article in Materials Today Chemistry (2025) entitled “Facile Access to Tetrazoles and 1-Substituted Benz(imidazoles) Using Zerovalent Copper Nanoparticles as an Inexpensive and Efficient Nanocatalyst and its Anticancer Study”. In the present work, three support materials, namely dendritic fibrous nano-silica (DFNS), hydroxyapatite (HAP), and Zn-Al layered double hydroxide (ZnAl-LDH), have been synthesized, and bimetallic PdxCu1-x nanoparticles were decorated on these solid supports by a simple sonication method. The structure and composition of all examined nanocomposites were studied in detail through various spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Nanocomposites with DFNS support, namely 10 wt% Pd0.75Cu0.25@DFNS and 30 wt% Pd00.25Cu0.75@DFNS, exhibited excellent catalytic activity in the synthesis of benzoxazole and tandem Sonogashira-cyclization reaction for benzofuran derivatives, respectively. The DFNS-impregnated bimetallic nanocomposites showed good stability and selectivity in synthesizing these derivatives, followed by recyclability up to five cycles without substantial loss in the catalytic activity, demonstrating possible industrial applicability. The outstanding benefits of these nanocomposites are mild reaction conditions, short reaction times, easy work-up, and excellent yields. Furthermore, HAP and ZnAl-LDH support, as well as their respective nanocomposites (15 wt% Pd0.75Cu0.25@HAP and 15 wt% Pd0.75Cu0.25@ZnAl-LDH), were subjected to bioactivity studies for colorectal cancer cells. The nanocomposites significantly reduced cell migration, indicating enhanced anti-metastatic potential against colorectal cancer cells. The studied nanocomposites can be employed for various organic transformations and bio-medical applications, which paves the way to achieve industrial feasibility.
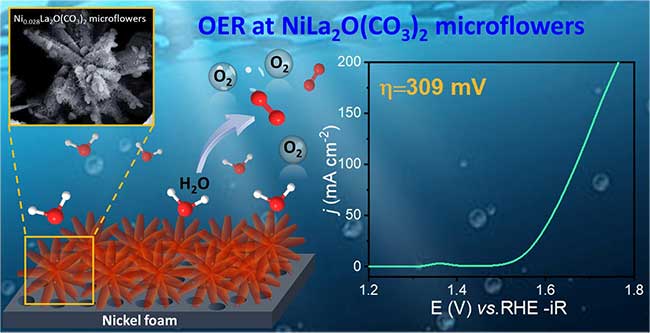
- Dr. Akshaya K. Samal and collaborators published a research article in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2025), entitled “Structural Transformations in Nickel-Doped Lanthanum-Based Electrocatalyst for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction”. This study focuses on optimizing and stabilizing the lattice structure by reducing lattice formation energy. At lower doping levels, the material exhibits thick and broad petal-like morphologies, which gradually evolve into thinner, sharper petals as the dopant concentration increases. This morphological transformation suggests that an optimal dopant concentration enhances electron redistribution and increases the density of active sites. Overall, this work highlights a clear relationship between Ni doping levels and the stabilization of La-based lattice structures. It also highlights the importance of dopant concentration and calcination in shaping the morphology and improving the electrocatalytic performance, providing valuable insights into the structural and chemical design of efficient OER electrocatalysts.
-
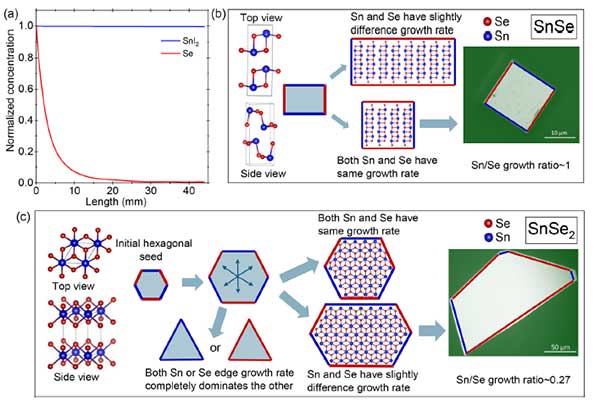
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak’s research group has recently published a research article in Advanced Materials Interfaces (2025) e00239, titled “In Situ Simultaneous Growth of Layered SnSe₂ and SnSe: A Linear Precursor Approach”. In this work, the team reports the successful in situ simultaneous growth of two structurally and functionally distinct tin selenide phases—SnSe₂ and SnSe—using a hot-wall chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method with a linear precursor strategy. This novel approach allows precise control over phase formation, enabling the co-existence of SnSe₂ (a layered semiconductor) and SnSe (a thermoelectric material) in a single synthesis step. The study not only provides new insights into the competitive growth dynamics of layered chalcogenides but also opens up avenues for the phase-engineering of 2D materials tailored for optoelectronic and thermoelectric applications
Dr. Ramesh Dateer and Collaborators published the research article in Catalysis Science and Technology (2025) entitled "Sustainable copper nanocomposite for multicomponent synthesis of triazolo quinolines and triazolyl benzamide derivatives and their bioactivity study” Herein, they report an efficient methodology for the preparation of a heterogeneous sustainable magnetically separable Cu@PANI@Fe3O4 nanocomposite, and its catalytic efficiency in multicomponent reactions for the synthesis of triazolo quinolines and triazolyl benzamide derivatives is investigated. A detailed mechanistic investigation by control experiments and DFT calculations has been performed to validate the proposed mechanism. Additionally, anti-cancer studies of the synthesized triazolo quinoline derivatives were performed and they were screened against colon carcinoma cell lines (HCT116) and subjected to MTT assay, showcasing good activity against the cells with IC50 of 28–45 μM. Further, gram-scale synthesis, recyclability of the nanocomposite and its utility in up to five consecutive cycles were deliberated.

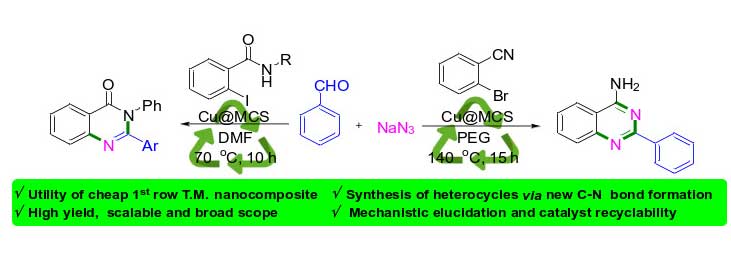
Dr. Ramesh Dateer and Collaborators published the research article in Materials Today Chemistry (2024) entitled “An expedient access to aminoquinazolines and quinazolinones via N-atom insertion reaction using copper nano particles decorated on magnetic carbon spheres” Here they discussed, new sustainable method for producing copper nanoparticles decorated on magnetic carbon spheres (Cu@MCS) using reduction method for the first time. Additionally, an investiga tion was conducted to assess the catalytic efficiency of Cu@MCS for the synthesis of pharmaceutically significant 4-aminoquinazolines and quinazolinone derivatives.
-
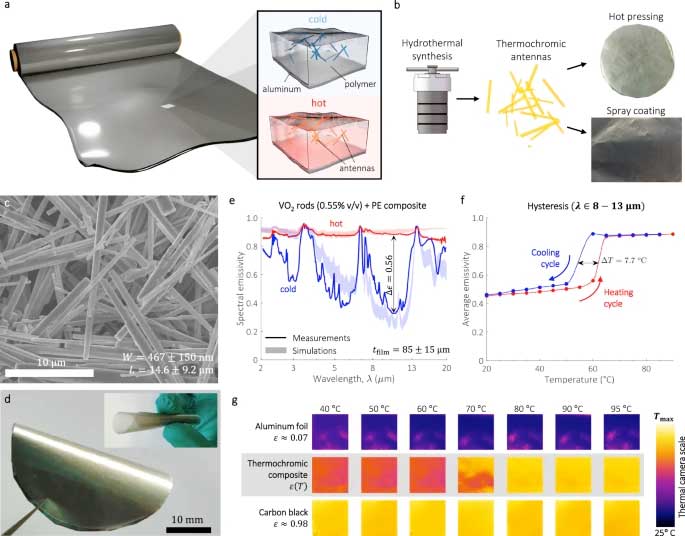
Dr. Gurunath Kargal and collaborators published a research article in Nature Communications (2024) entitled "Infrared thermochromic antenna composite for self-adaptive thermoregulation". Self-adaptive thermoregulation, the mechanism living organisms use to balance their temperature, holds great promise for decarbonizing cooling and heating processes. This functionality can be effectively emulated by engineering the thermal emissivity of materials to adapt to background temperature variations. Yet, solutions that marry large emissivity switching (Δε) with scalability, cost-effectiveness, and design freedom are still lacking. Here, we fill this gap by introducing infrared dipole antennas made of tunable thermochromic materials. We demonstrate that non-spherical antennas (rods, stars and flakes) made of vanadium-dioxide can exhibit a massive (~200-fold) increase in their absorption cross-section as temperature rises. Embedding these antennas in polymer films, or simply spraying them directly, creates free-form thermoregulation composites, featuring an outstanding Δε ~200 fold in spectral ranges that can be tuned at will. Our research paves the way for versatile self-adaptive heat management solutions (coatings, fibers, membranes, and films) that could find application in radiative-cooling, heat-sensing, thermal-camouflage, and other.
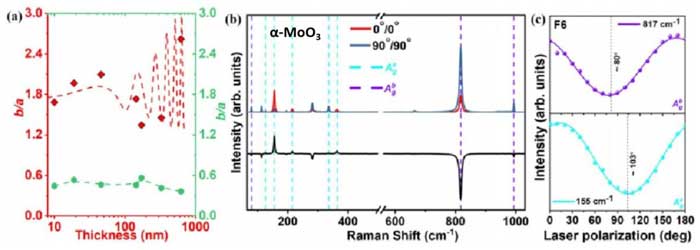
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak’s group published a research article in Physical Review B (2024) 110, 085423 entitled “ Chiral phonon and in-plane Raman optical activity of anisotropic layered α-MoO3 ”. This work provides the distinction of chiral phonon modes in α-MoO3 and its in-plane anisotropic nature, which can assist in the development of polarization-sensitive photonic devices and nonlinear optoelectronics.
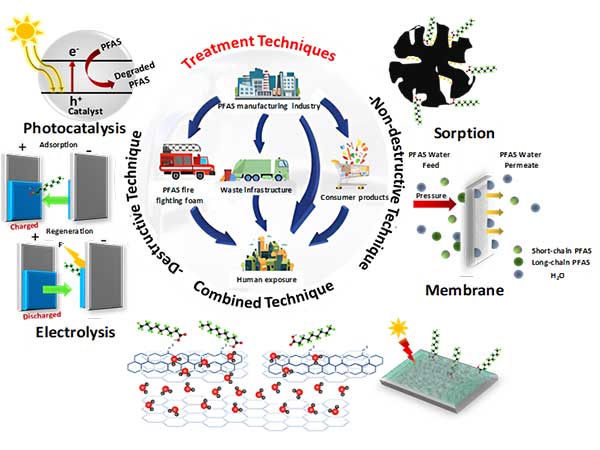
Dr. Akshaya K. Samal and collaborators published a research article in Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering (2024), entitled “Mitigating PFAS Contaminants in Water: A Comprehensive Survey of Remediation Strategies”. The review examines various methods for removing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) which are highly stable compounds with strong carbon-fluorine bonds. The review covers sorption techniques, membrane separation approaches, and hybrid methods with mechanisms like size exclusion, electrostatic interactions, fluorous interaction, and adsorption responsible for effectively eliminating PFAS. The article also discusses the cost and energy considerations of different PFAS removal technologies, noting that advances in materials and processes have reduced costs and improved efficiency. Despite these advancements, the challenges still remain in handling short chain, low concentrations and optimizing sorbent regeneration. The study emphasizes the need to enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of hybrid remediation methods to overcome such challenges.
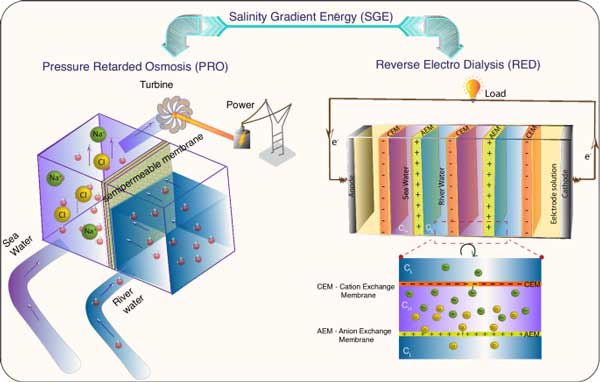
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak’s group published a review article in npj 2D materials and applications (2024) 8, 47 (one of the Nature sister journals)entitled “Salinity gradient induced blue energy generation using two-dimensional membranes”. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the fundamental principles behind the salinity gradient energy (SGE) and explain how the 2D nanoporous membranes can make SGE a viable source of energy.
Dr. Pramoda K. Nayak wrote a book titled “Two-Dimensional Quantum Materials”, which was published in Cambridge Scholars Publishing, Lady Stephenson Library, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE6 2PA, UK with ISBN: 978-1-0364-0600-4 (2024). This book provides a comprehensive exploration of the fascinating world of 2D materials and their implications in the realm of quantum phenomena and applications. It delves into the multifaceted aspects of 2D materials, from their fundamental properties to cutting-edge applications, promising to provide valuable insights into the forefront of nanoscience and technology.

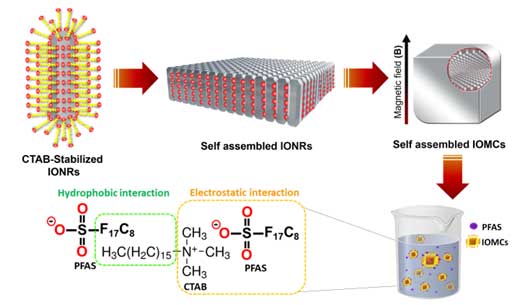
Dr. Akshaya K. Samal and collaborators published a research article in ACS Langmuir (2024), entitled “Transformative Dynamics: Self-Assembly of Iron Oxide Hydroxide Nanorods into Iron Oxide Microcubes for Enhanced Perfluoroalkyl Substance Remediation”. This process involves a complex interplay between kinetics and thermodynamics parameters to explore the nucleation, self-assembly, and growth mechanisms. In this reported work, kinetic investigations were carried out to gain insights into the dynamics of magnetic properties during the self-assembly process. This study also provided a new approach and insights into the importance of tuning the facets and magnetic properties of iron oxide microcubes to remediate per and polyfluorinated substances. These insights unlock new avenues in surface chemistry offering innovative approaches for environmental remediation.
Dr. Akshaya K. Samal and collaborators published a research article in Journal of Water Process Engineering (Elsevier, 2024), entitled "Anisotropic Cu2O Nanostructures: A Promising Remediation for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances." Our research delves into the fascinating field of surface chemistry. This present study sheds light on tuning a controlled growth and morphology of Copper oxide (Cu2O) nanostructures at the nanoscale level. In this study, we have meticulously tailored the surface and facet orientation of Cu2O nanostructures to improve their efficacy in remediating environmental contaminants such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). This study provides significant insights into the interaction mechanisms between Cu2O nanostructures and PFAS, underscoring the critical role of surface and optical modifications in optimizing nanostructures for environmental remediation applications.
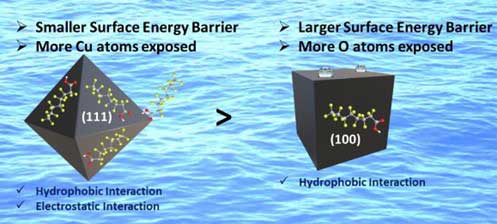
Dr. Pramoda K. Nayak and collaborators published a research article in Applied Physics Letters (2024), 124, 033103 entitled “Robust valley quantum coherence in synthetic 3R-phase MoS2: A material for future valley based Devices”. This work paves the way toward using 3R-phase MoS2 as a key material for the development of future quantum technologies utilizing valley polarized photons
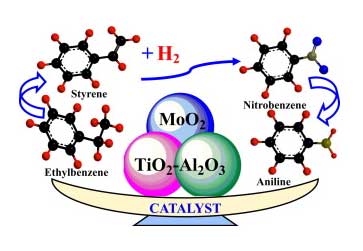
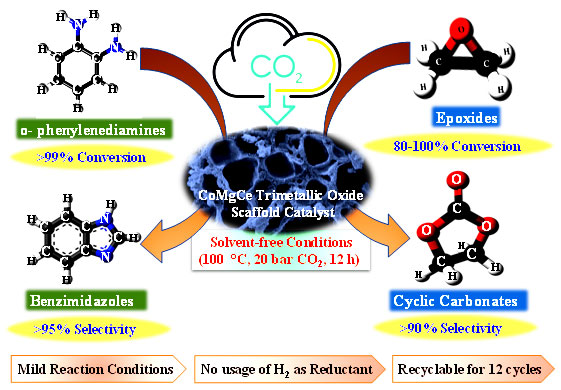
Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav and collaborators published a research article in ACS Applied Nano Materials (2024)entitled “Hollow CeO2 Nanospheres as Catalyst for the Conversion of Aromatic Diamines to Benzimidazoles.” This work gives a brief demo of a selective strategy for CO2 fixation into the value-added product “benzimidazole” by employing highly recyclable hollow CeO2 nanospheres (HNS-CeO2) as an efficient catalyst.
Prof. Siddappa A. Patil published a review article in ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3(8), 2009-2023 entitle with “Recent Advances in the Removal of Radioactive Iodine and Iodide from the Environment”. This review provides the information about the current advancements in the removal of iodine and iodide from human-made contaminated aqueous waste.
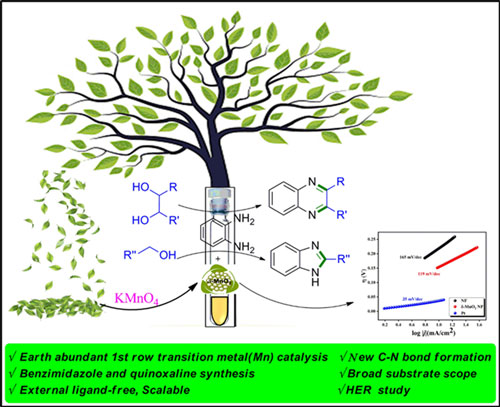
Dr. Ramesh Dateer and collaborators published a research article in Langmuir 2023 (ASAP) entitled with “Room Temperature Synthesis of Biogenic δ-MnO2 NPs for the Dehydrogenative Coupling of Diamines with Alcohols for Benzimidazoles and Quinoxalines Synthesis: An Efficient Catalyst for Electrochemical Application” in which they have reported An efficient, unique and eco-friendly biogenic synthesis of single crystalline δ-phase manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO2 NPs) using Gliricidia sepium leaves (GSL) extract at room temperature has been revealed for the first time. The reactivity of synthesized catalyst was demonstrated by achieving a one-pot synthesis of benzimidazoles and quinoxalines via acceptorless dehydrogenative coupling (ADC) strategy utilizing bio-renewable alcohols. Importantly, the δ-MnO2 NPs catalyst exhibited superior catalytic activity and high durability towards hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline media highlighting the dual use of catalyst.
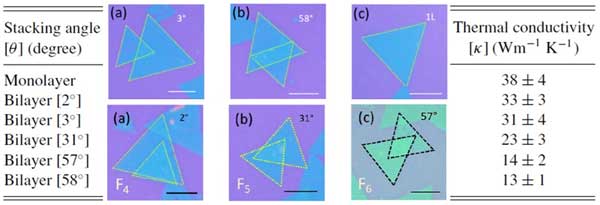
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak published a research article in Physical Review B(2023), 108, 115439 entitled “Probing angle-dependent thermal conductivity in twisted bilayer MoSe2”. This work provides the platform towards tuning the angle-dependent thermal transport in any bilayer 2D systems and shows a significant paradigm for device modeling and other applications.
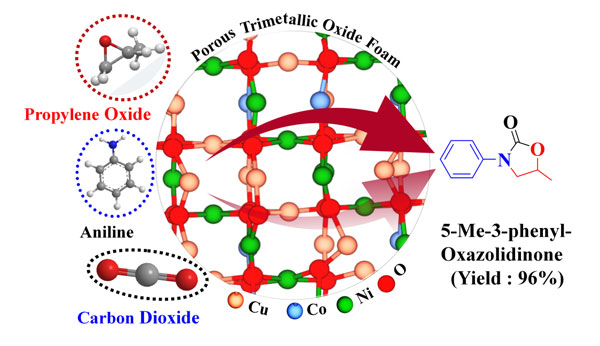
Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav group published a research article in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 15.18 (2023): 21994–2011 entitled “ Trimetallic Oxide Foam as an Efficient Catalyst for Fixation of CO2 into Oxazolidinone: An Experimental and Theoretical Approach”. This work gives a brief demonstration of a selective one-pot strategy for CO2 fixation into oxazolidinone by employing stable porous trimetallic oxide foam as a new catalyst. A doubly synergistic plausible reaction mechanism was proposed for the oxazolidinone synthesis experimentally with the support of a DFT study. Very interestingly, the PTOF catalyst could be significantly reused for up to fifteen consecutive cycles with stable activity and retention of physicochemical properties.
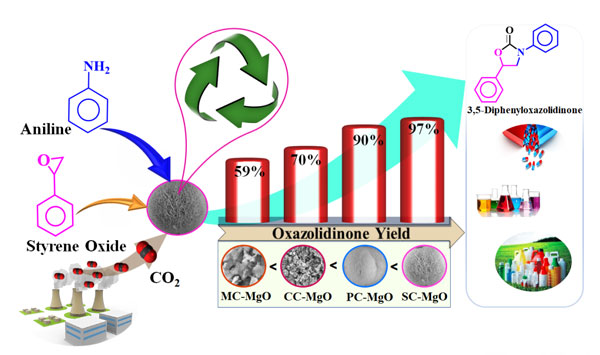
Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav group published a research article in Energy & Fuels entitled “Base-Tailored Hierarchical MgO Microspheres as an Efficient Catalyst for CO2 Fixation into Oxazolidinone at Atmospheric Pressure” . This study describes a solvent and co-catalyst-free CO2 fixation reaction employed by efficient hierarchical magnesium oxide microspheres. A straightforward precipitation process was assisted for the synthesis of base-MgO materials using different precipitating agents namely, Na2CO3, K2CO3, MgCO3, and Cs2CO3. We developed a highly feasible CO2 fixation process using a recyclable MgO catalyst for the oxazolidinone synthesis.
Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav group published a research article in Energy & Fuels 37.2 (2023): 1187-1206 entitled “Stable Engineered Trimetallic Oxide Scaffold as a Catalyst for Enhanced Solvent-free Conversion of CO2 into Value-added Products”.This work demonstrates the development of mesoporous trimetallic oxide scaffolds as heterogeneous catalyst for the solvent-free transformation of CO2 into various value-added products. Also, this work provides a new and greener route for the synthesis of benzimidazoles and organic carbonates, which can be easily adapted for scale-up applications.
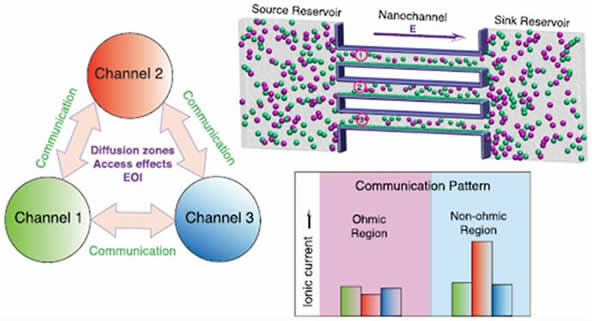
Dr. Pramoda Kumar Nayak published a research article in ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 11640−11650 entitled with “All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Communication Between Nanochannel Arrays”. This work provides new insights for designing the nanochannel arrays to scale up the nanoscale phenomena and improve the process efficiency for various applications involving ion transport characteristics.
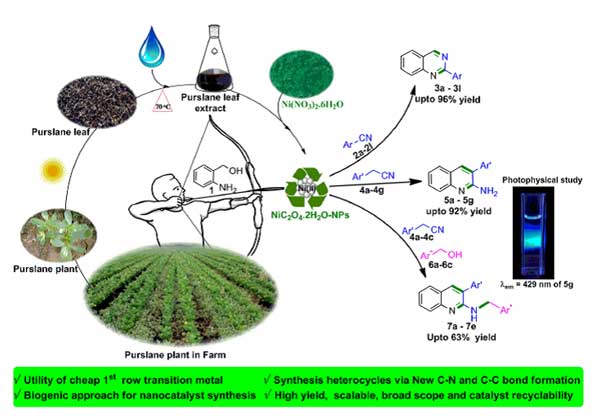
Dr. Ramesh Dateer and collaborators published a research article in New J. Chem., 2023,47, 8268-8276 entitled with “A Sustainable Approach for Nickel Nanoparticles Synthesis: An Expeditious Access to N-heterocycles under Heterogeneous Condition and its Photophysical studies” in which they have reported A sustainable and environmentally benign biogenic technique for one-step synthesis of Ni-NPs (NiC2O4.2H2O-NPs) using Portulaca oleracea (purslane) leaves extract has been disclosed for the first time. Importantly, the photophysical property studies of the synthesized N-heterocycles is deliberated and gram scale synthesis was achieved. Moreover, catalyst recyclability, control experiments, mechanistic elucidation was elaborated.
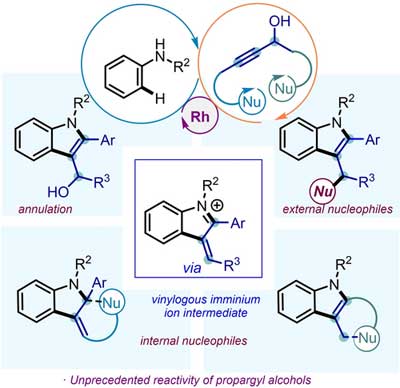
Dr. Manoj Mane and collaborators published a research article in Chemistry—A European Journal 2023, 29, e202203055 entitled with "Merging Rh-Catalyzed C-H Functionalization and Cascade Cyclization to Enable Propargylic Alcohols as Three-Carbon Synthons"
Dr. Manoj Mane and collaborators published a research article in European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2023, 26, e202201466 entitled with "Ruthenium-Catalyzed Regioselective 1, 2-Hydrosilylation of N-Heteroarenes"

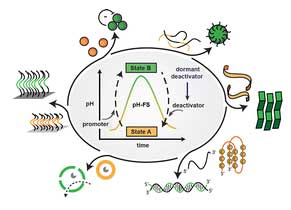
- Dr. Indrajit Maity and collaborators published a review article in Chemical Communications, 2023, 59, 1125-1144 entitled with "pH Feedback Systems to Program Autonomous Self-Assembly and Material Lifecycles"
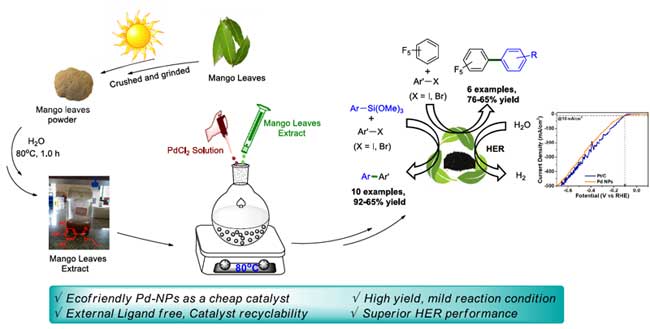
- Dr. Ramesh Dateer and collaborators published a research article in Catalysis Letter 2022, 1-17 entitled with “Greener Approach for Pd–NPs Synthesis Using Mangifera Indica Leaf Extract: Heterogeneous Nano Catalyst for Direct C–H Arylation of (Poly) Fluorobenzene, Hiyama Coupling”
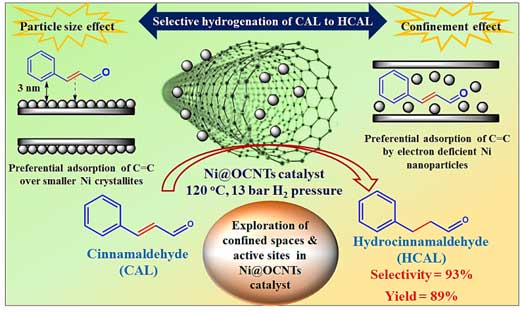
- B.M. Nagaraja and his group published a research article in Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering in which they reported on “Exploring the Confined Space and Active Sites of [email protected] Catalyst for Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to Hydrocinnamaldehyde”
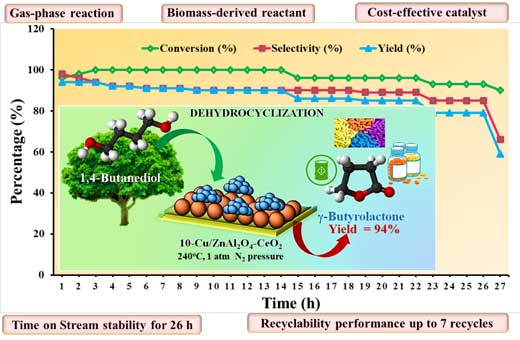
- B.M. Nagaraja and his group published a research article in Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 106 (2022) 142-151 in which they reported on Selective Vapour-Phase Dehydrocyclization of Biomass-Derived 1,4-Butanediol to γ-Butyrolactone over Cu/ZnAl2O4-CeO2 Catalyst
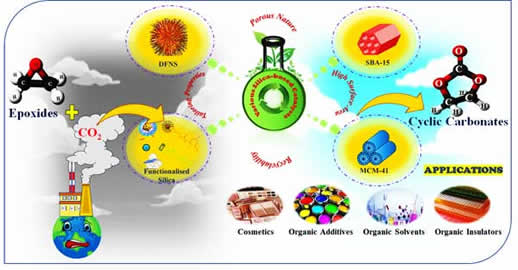
- Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav’s group and collaborators published an original review article entitled "Recent Developments in State-of-the-art Silica-Modified Catalysts for Fixation of CO2 into Epoxides to Organic Carbonates" in RSC "Sustainable Energy & Fuels" Journal (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SE01916C). The review article provides a panoramic overview which engulfs understanding catalytic strategies for CO2 fixation reactions with heterogeneous state-of-the-art modified silica-based materials.
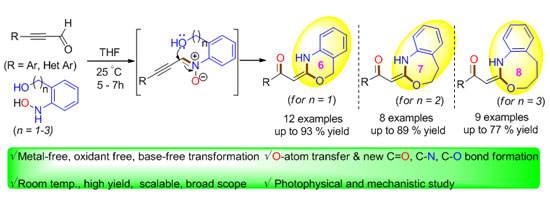
- Dr. Ramesh B. Dateer’s group and collaborators published an article in ‘Organic Letters’ 2021 on “Catalyst- and Additive-Free Approach to Construct Benzo-oxazine, Benzo-oxazepine and Benzo-oxazocine: O-Atom Transfer, New C=O, C-N and C-O Bond Formation at Room Temperature”.
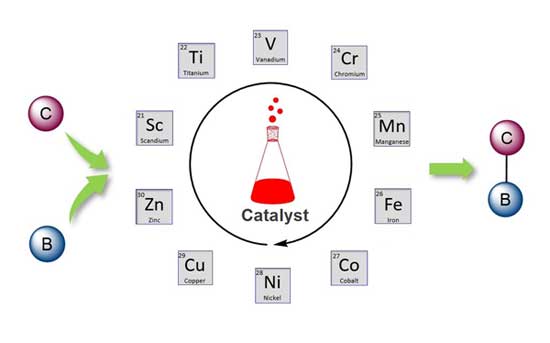
- Dr. Shubhankar Kumar Bose and collaborators published an article in Chem. Rev. 2021 (DOI 10.1021_acs.chemrev.1c00255) on "First-Row d-Block Element-Catalyzed Carbon−Boron Bond Formation and Related Processes". This review surveys the current state-of-the-art in the use of first-row d-block element-based catalysts for the formation of carbon-boron bonds
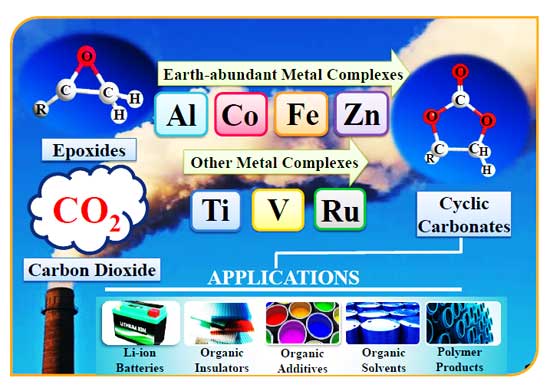
- Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav’s group and collaborators reviewed the employment of state-of-the-art metal complexes as promising catalytic systems to assess sustainable transformation of CO2 into value-added products. The review article summarizes the recent advances with Earth-abundant metals such as aluminum, cobalt, iron, zinc and few other transition metals in association with different ligand skeletons used for the structural construction of their respective complexes. The review sequentially categorizes these complexes and provides a panoramic overview of their selective catalytic activities for the fixation of CO2 into epoxides to cyclic carbonates and mechanistic understandings based on experimental and theoretical evidences.
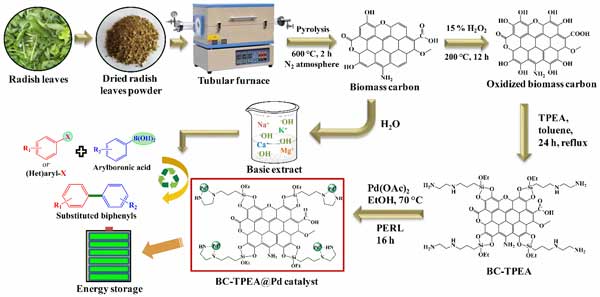
- Dr. Siddappa A. Patil and his group published research article in Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 570, 151156 in which they reported agricultural waste biomass-derived carbon-supported palladium-based ([email protected]) heterogeneous catalyst through a green and sustainable approach by utilizing radish leaves as bio-waste resources and explored its catalytic activity in external base free Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling and energy storage applications.
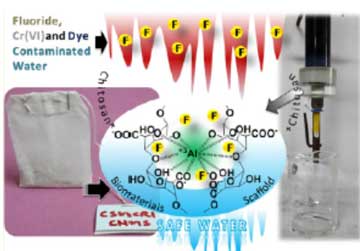
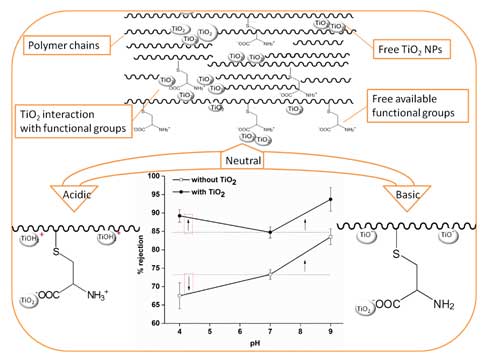
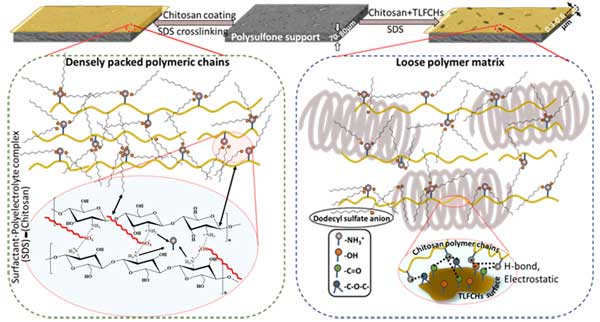
- Developing Helical Carbon Functionalized Chitosan-based Loose Nanofiltration Membranes for Selective Separation and Wastewater Treatment
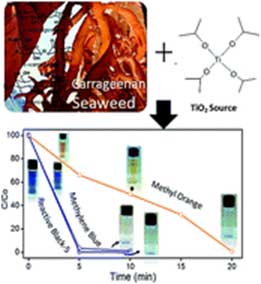
S.K. Nataraj, Mahaveer Halakarni and Team developed has published original article in Chemical Engineering journal where Team developed highly water stable biopolymer-based loose nanofiltration membrane is prepared, wherein the selective permeability of salt and dyes is governed by judicial utilization of bio-based highly oxygenated carbon helices as fillers.
- Prof. Chandra Sekhar Rout’s group and collaborators reviewed spinel MnCo2O4-based materials for energy storage and conversion applications. In this review, the use of low cost and abundant multifunctional materials for the development of supercapacitor devices and batteries were summarized. Completely, the design of electrocatalysts for water splitting and capable to proportionate the tetra-electronic process of oxygen reduction reaction are reviewed, including the main strategies in the preparation of these materials and considering their key multifunctional role in the way to a more sustainable society.
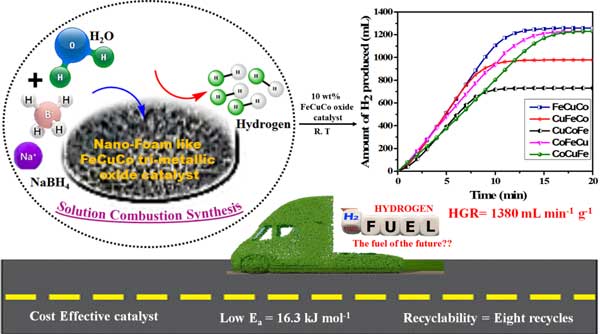
- B.M. Nagaraja and Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav group published a research article in Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130988 in which they reported on Engineered Nano-Foam of Tri-Metallic (FeCuCo) Oxide Catalyst for Enhanced Hydrogen Generation via NaBH4 Hydrolysis.
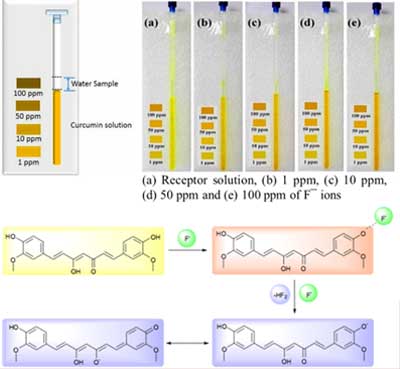
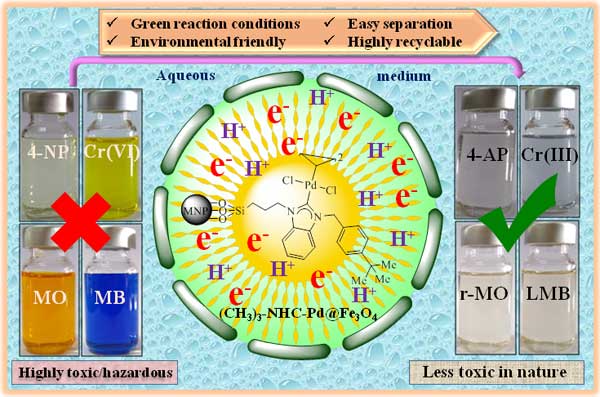
- Dr. Siddappa A. Patil and his group published research article in J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 189-204 in which they reported efficient and recyclable palladium enriched magnetic nanocatalyst for reduction of toxic environmental pollutants such as toxic 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)), methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) at room temperature in aqueous media.
- Bose et al. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, DOI: 10.1002/adsc.202001616
A table of contents entry:
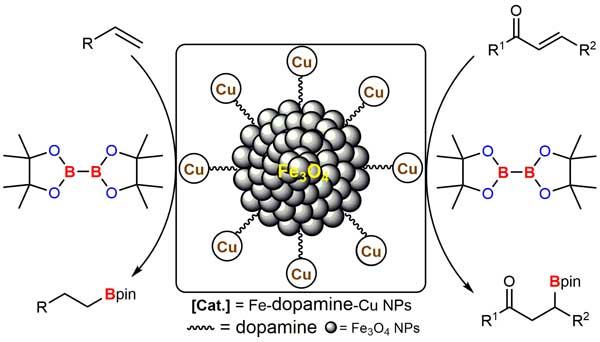
Shubhankar Kumar Bose et al. developed an efficient, easy to recover and reusable nano-ferrite-supported Cu nanoparticles (Fe-dopamine-Cu NPs) catalyzed anti-Markovnikov-selective hydroboration of alkenes and β-borylation of α,β-unsaturated ketones and ester. This work was published in Adv. Synth. Catal. and designated as Very Important Publication (VIP) & featured in the inside cover of the ASC special issue on boron.
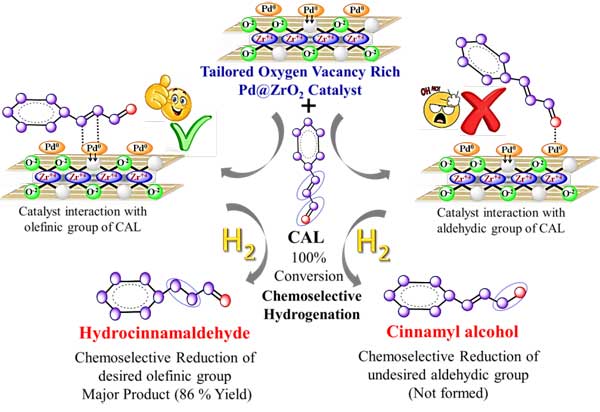
- B.M. Nagaraja and Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav group published research article in New Journal of Chemistry 2021, 45, 5659-5681 in which they reported on Chemoselective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over a tailored oxygen-vacancy-rich [email protected] catalyst
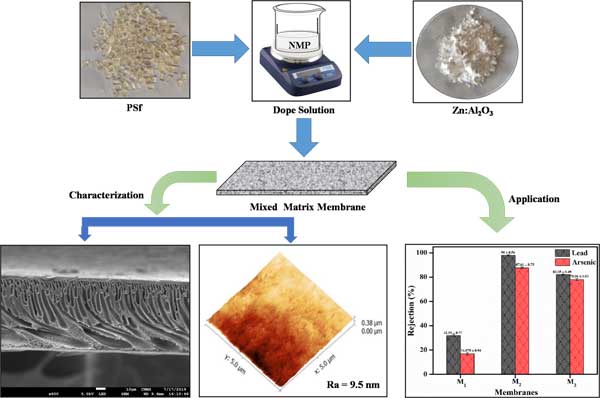
- Mahesh Padaki and his group developed Fe doped Al2O3 nanoparticles by novel and sustainable solution combustion approach afterwards nanoparticles were incorporated into the polymeric matrix. The fabricated mixed matrix membranes had essential role in water purification by enhancing antifouling property along with that the trade-off relationship between the selectivity and productivity. These results are published in Chemosphere.
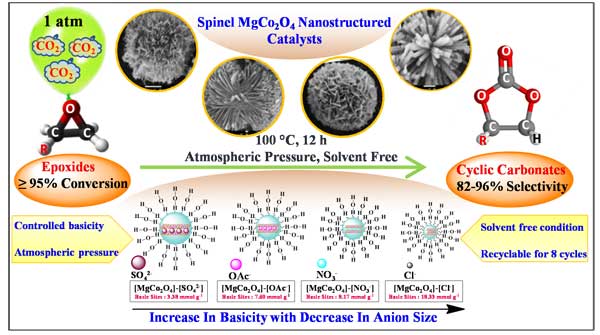
- Dr. Arvind H. Jadhav and his group for the first-time explored basicity controlled MgCo2O4 nanostructures as a competent heterogeneous catalytic system for fixation of CO2 into epoxides and form cyclic carbonates at atmospheric pressure. The effect of different interlayer anions (chloride, nitrate, acetate and sulphate) on morphology, surface area and exposed Lewis basic (O2-) sites were studied in detail. Further, catalytic activity studies revealed that [MgCo2O4]-[Cl-] catalyst in presence of base gave the most outstanding results under mild reaction conditions (100 ℃, 1 atm, 12 h) and various reaction parameters were investigated to optimize reaction conditions. Interestingly, the catalyst also showed good tolerance for a broad substrate scope and could be easily recycled for eight consecutive cycles. These results are published in CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL.
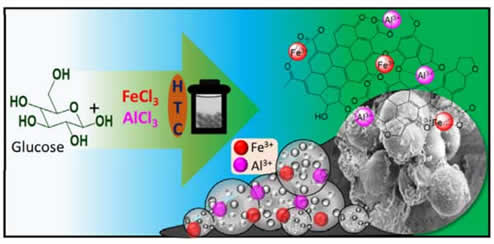
- S.K. Nataraj et al have formulated "Fe-Al based nanocomposite reinforced hydrothermal carbon: Efficient and robust absorbent for anionic dyes" and the results were published in Chemosphere
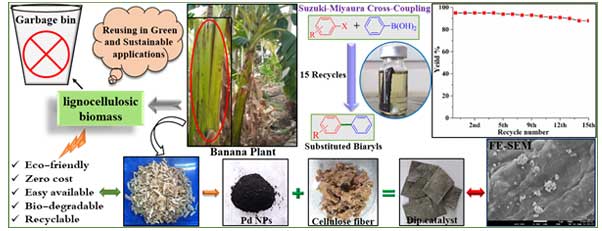
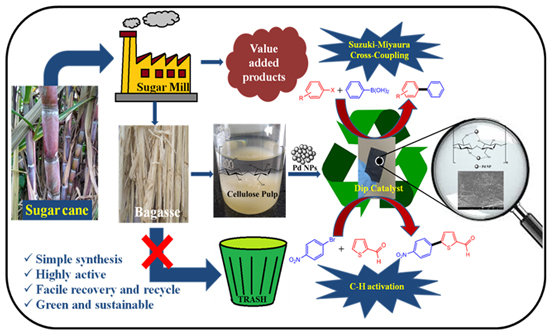
- Dr. Siddappa A. Patil and his group developed a green and sustainable approach for the synthesis of palladium nanoparticles decorated cellulose fibers as dip catalyst by utilizing bio-waste resources. The fabricated dip catalyst had essential key features such as eco-friendly, cost effective, easy availability, highly active and selective towards Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. The dip catalyst shows excellent catalytic performance and great tolerance for synthesis of various functional groups substituted biaryls under green reaction conditions. Dip catalyst can be reused more than 15 recycles in cross-coupling reactions without lacking in catalytic activity. The details can be found in the published article in "Cellulose”.
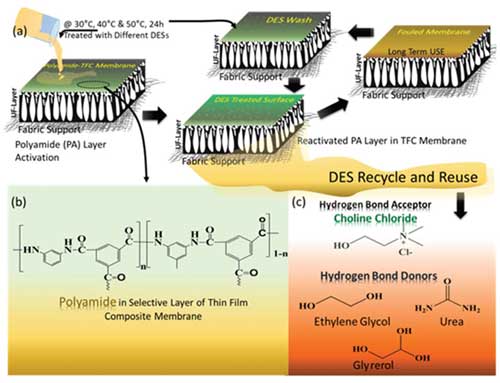
- S.K. Nataraj et al., Published original article in Green Chemistry 2020,22, 2381 – 2387 in which they explore novel washing solutions for commercial RO membranes, which not only the clean the membrane but also enhances the overall performance.
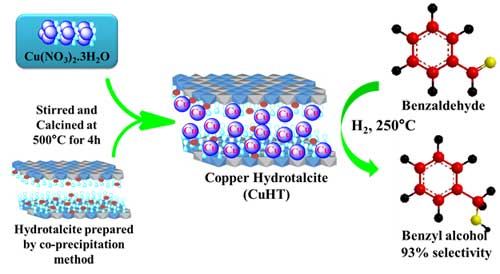
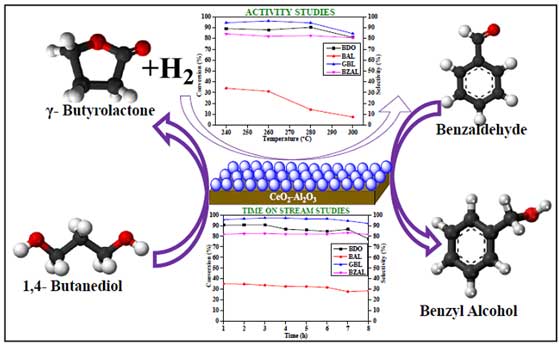
- B.M. Nagaraja and his group reports successfully carryout 1,4-butanediol dehydrogenation and benzaldehyde hydrogenation simultaneously over ceria-alumina supported copper (Cu/CeO2-Al2O3) catalyst. In this concern, 10 wt.% of Cu supported on CeO2-Al2O3 (3:1 ratio) was synthesized using wet impregnation method. The best results were obtained with 10 wt.% of Cu supported on CeO2-Al2O3 (3:1 ratio) catalyst with benzaldehyde conversion of 34% and 84% selectivity of benzyl alcohol. The conversion of 1,4-butanediol was seen to be 90% with around 95% selectivity of γ-butyrolactone. In terms of permanence, the Cu/CeO2-Al2O3 (10CCA) catalyst was quite steady and showed stable activity up to 24 h in time on stream profile.
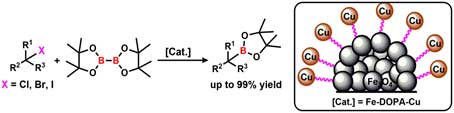
- Dr. Shubhankar Kumar Bose et al. Green Chem., 2020, 22, 2799–2803. An efficient, easy to recover and reusable Cu nanocatalyst (Fe-DOPA-Cu) system has been developed for the borylation of alkyl halides, including benzyl chlorides and bromides with diboron reagents.
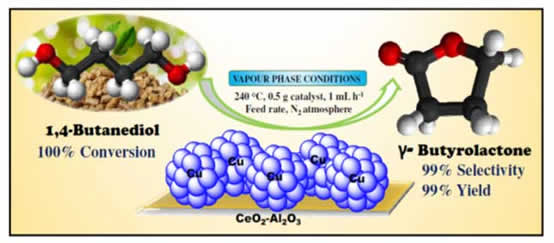
- B.M. Nagaraja and his group reports successfully carryout Mesoporous copper based ceria-alumina catalysts prepared by wet impregnation method were used for dehydrogenation of 1,4-butanediol to γ-butyrolactone. The reaction was carried out under vapour phase conditions in the temperature range of 240–300 °C. The better activity results observed using 10 wt% copper supported over ceria-alumina (75:25) catalyst wherein 1,4-butanediol showed a conversion of 100% and selectivity towards γ- butyrolactone was 99% at 240 °C. The activity was due to synergistic effect of alumina and ceria support along with the presence of highly basic sites and other physico-chemical properties. In terms of stability, the catalyst is stable activity upto 24 h.
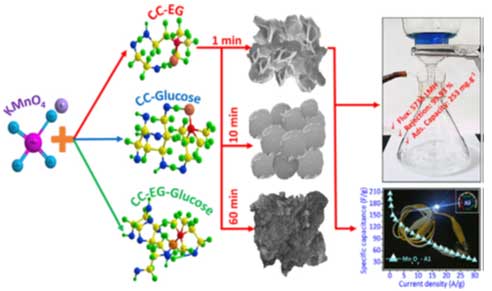
- Nataraj and Dibyendu et al published research article in Chemical Engineering Journal on designed multifunctional nanomaterial via ultrafast synthesis (15 Seconds) protocol to produce exfoliated manganese oxides for water purification and energy storage. (Chemical Engineering Journal 379 (2020) 122327.)
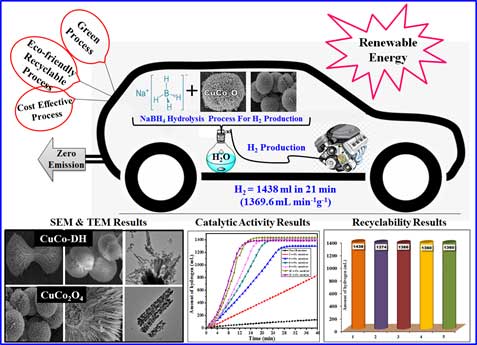
- B.M. Nagaraja and his group reports successfully synthesized copper-cobalt double hydroxide precursor and the resultant CuCo2O4 spinel catalyst. The CuCo2O4 spinel catalyst was then tested for its application in hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis by performing the reaction using 10 wt% of CuCo2O4 spinel catalyst and 0.5 g NaBH4 at room temperature. The CuCo2O4 spinel catalyst with tailored architecture displayed high catalytic activity with H2 generation rate of 1370 mL min-1 g-1 (1438 mL in 21 min). Further, recyclability study of CuCo2O4 spinel catalyst was also performed which displayed good catalytic activity and stability even after five successive recycles.
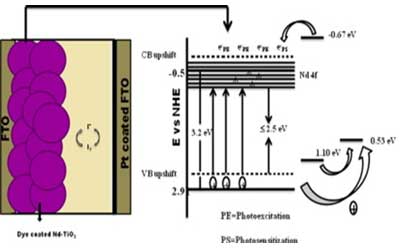
- Dr. Chandra Sekhar Rout’s group and collaborators reported the fabrication of 3D self-supported heterogeneous NixSey cubic-orthorhombic nanocrystals grown by a facile one-step chemical vapour deposition (CVD) approach on Ni foam substrates for high performance supercapacitor electrode applications. For the first time crystalline NixSey is synthesized by CVD, and demonstrates outstanding electrochemical performances with high specific capacitance of 1333 Fg-1 at a current density of 27 Ag-1, ultra-high energy density (105 W h Kg-1) at power density (54 kW Kg-1) and an excellent operational stability. The details can be found in the published article in “Dalton Transactions” and is highlighted in the cover page of the journal.

- Dr. Siddappa A. Patil and his group developed a green and sustainable cellulose-based dip catalyst. The activity of the dip catalyst was studied for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction and was found to give excellent conversion with 15 recycles. Further, the activity of dip catalyst in C5-arylation of 2-substituted thiophenes was evaluated for which promising yields were obtained.
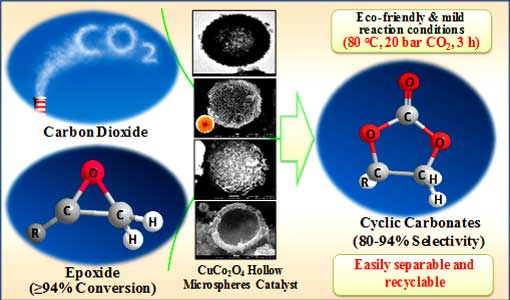
Dr. Arvind H Jadhav, B.M. Nagaraja and his group reports successfully synthesized hollow marigold CuCo2O4 spinel microspheres by a facile solvothermal method and employed as catalyst for the chemical fixation of CO2 and epoxide into cyclic carbonate under solvent-free conditions. The model reaction of styrene oxide and CO2 using 50 mg CuCo2O4 as catalyst and 8 mol% of TBAI as base was found to be an efficient catalytic system at 80 °C, 20 bar and 3 h of reaction time. A high conversion of 94% and selectivity of 94% was obtained under the mild optimized reaction conditions.
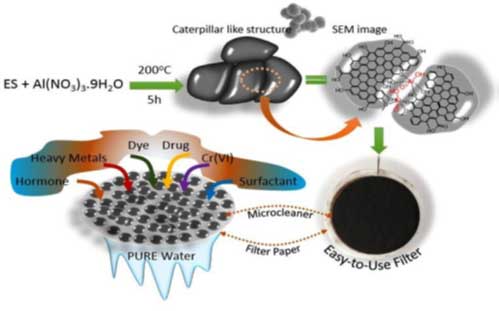
S.K. Nataraj, D. Mondal and their team developed novel functional nanocomposite materials for treating surface water which adulterated by hazardous pollutants such as dyes, pharmaceutical 3 wastes, surfactants, heavy metals, hormones, etc. The same as published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
|
|